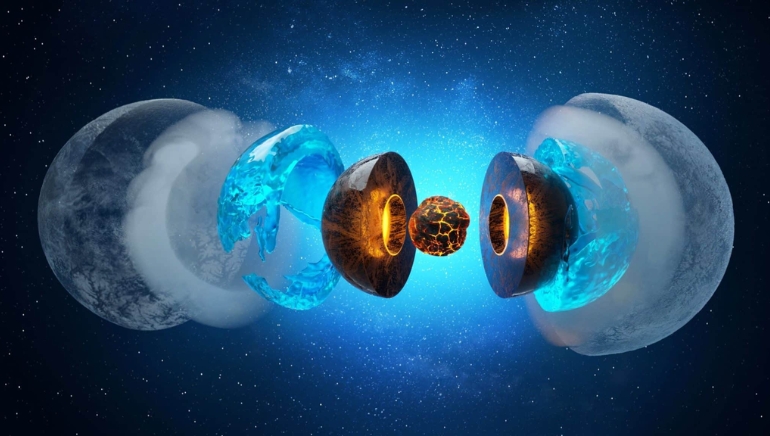
In a groundbreaking revelation, scientists from Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois, have unearthed a colossal reservoir of water hidden deep within the Earth’s mantle, approximately 700 kilometers below the planet’s surface. This astonishing discovery challenges conventional theories about the origin of Earth’s water and opens a new chapter in our understanding of the planet’s geological processes.
The newly found subterranean ocean, which dwarfs all the Earth’s surface oceans combined, was uncovered by researchers seeking to unravel the mysteries of Earth’s water sources. Encased within ringwoodite, a unique blue-hued rock, this hidden ocean defies previous assumptions about the distribution of water within the Earth.
Dr. Steven Jacobsen, the lead researcher behind this remarkable find, affirms, “This constitutes significant evidence supporting the notion that Earth’s water originated internally.” The discovery not only sheds light on the planet’s geological history but also prompts a reevaluation of existing theories regarding the Earth’s water cycle.
To unveil the presence of this expansive underground ocean, scientists deployed a sophisticated network of 2000 seismographs across the United States. These instruments meticulously analyzed seismic waves generated by over 500 earthquakes, allowing researchers to peer deep into the Earth’s interior. As seismic waves traversed the mantle, they encountered regions of dampened rock, indicating the presence of the concealed water reservoir.
The implications of this discovery are profound. It suggests that Earth’s water may not have solely arrived through comet impacts, as previously hypothesized, but rather could have originated from within the planet itself. This challenges conventional wisdom and opens avenues for further research into the intricate mechanisms governing Earth’s water cycle.
Moreover, the existence of this subterranean ocean prompts a reassessment of the role of water in maintaining geological stability. Without such reservoirs deep within the Earth, water would predominantly reside on the planet’s surface, drastically altering its landscape and geological processes.
Excitement abounds among researchers as they plan to expand their seismic data collection efforts worldwide. By studying mantle melting and the distribution of water-rich regions, scientists aim to unravel the full extent of this hidden ocean and its impact on Earth’s geological dynamics.
In conclusion, the discovery of a gigantic ocean nestled deep within the Earth’s mantle challenges conventional theories and offers a tantalizing glimpse into the planet’s geological history. As scientists continue to delve deeper into the mysteries of our planet, they pave the way for a more comprehensive understanding of Earth’s water cycle and its fundamental role in shaping our world.